
Ear Infection
Ear Infection 👂
Ear infections are a common ailment, particularly in children, that can cause significant discomfort and concern. Medically termed as otitis media, these infections occur when the middle ear—the area just behind the eardrum—becomes inflamed, often due to bacterial or viral infections. Ear infections can be acute, with sudden and severe symptoms, or chronic, where infections recur frequently and may cause long-term damage to the ear.
The ear is a complex organ, divided into three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each section plays a vital role in hearing and balance. The middle ear, where most infections occur, is connected to the back of the throat by the Eustachian tube. This tube helps equalize pressure and drain fluids from the middle ear. When the Eustachian tube becomes blocked or swollen—often from a cold, allergy, or upper respiratory infection—fluid can build up, creating an ideal environment for germs to grow.
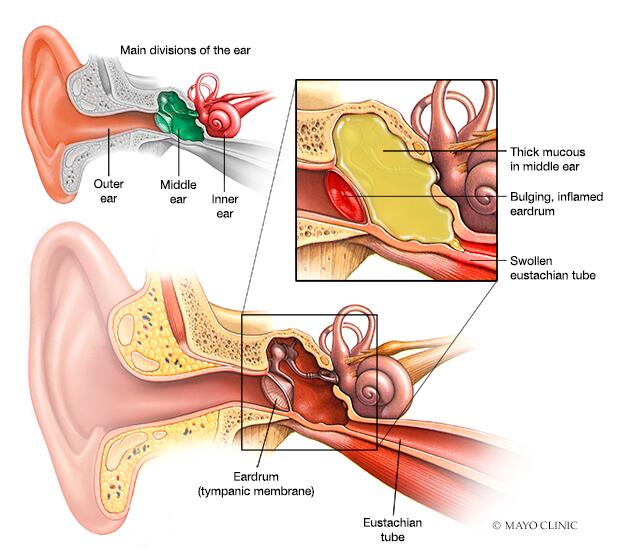
Ear infection
Ear infections are particularly prevalent among young children due to their shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes, which are more prone to blockage. Symptoms can include ear pain, fluid drainage from the ear, trouble hearing, and in severe cases, fever and irritability. While many ear infections resolve on their own, some may require medical intervention to prevent complications and preserve hearing.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ear infections is crucial for parents, caregivers, and individuals prone to this condition.
6 Sign and symptom of ear infection
- Pain in ear – One of the most common symptoms, ear pain can range from mild to severe. It is often described as a sharp, stabbing, or dull ache. The pain may be constant or intermittent and is usually more intense when lying down.
- Fever – A mild to moderate fever often accompanies ear infections, especially in children. This is the body’s response to fighting off the infection.
- Trouble hearing – Temporary hearing loss is common with ear infections due to fluid buildup in the middle ear. Sounds may seem muffled, and it might be difficult to hear quiet noises.
- Trouble sleeping – They may have difficulty sleeping or feeding due to the discomfort.
- Irritability & crying – Ear infections can make children and infants particularly irritable and fussy.
- Fluid drainage – Ear infections can cause fluid to drain from the ear. This fluid can be clear, yellow, or even bloody. If the eardrum has ruptured, the drainage might have a foul odor.
Oftentimes, young babies won’t be able to express their pain to their parents. Therefore, do watch out for behaviours like:
👉rub or pull their ear
👉not react to some sounds
👉be irritable or restless
👉be off their food
👉keep losing their balance
If the symptoms worsens, do consult your physician in order to examine the ear for inflammation or discharge.
Causes of ear infection
- Upper respiratory tract infection – Colds, sinus infections, and throat infections can lead to ear infections. These illnesses often cause inflammation and mucus production, which can block the Eustachian tube.
- Sudden changes in air pressure ✈️ – Sudden changes in air pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, can disrupt the Eustachian tube’s ability to equalize pressure, potentially leading to fluid buildup and increasing the risk of ear infections.
- Eustachian tubes are smaller than average, or have a blocked Eustachian tube – Smaller-than-average Eustachian tubes can easily become blocked or fail to drain fluid properly, increasing the risk of ear infections. This is particularly common in young children, whose Eustachian tubes are naturally shorter and more horizontal, making them more prone to blockage and fluid buildup.
- Young age as baby and children – Babies and young children are more prone to ear infections due to their shorter and more horizontally oriented Eustachian tubes, which can become easily blocked, leading to fluid accumulation and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Swimming in polluted water – Can introduce bacteria and contaminants into the ear canal, potentially causing irritation, inflammation, and increasing the risk of developing an ear infection.
- Failing to dry the outer ear properly after swimming or bathing – Can leave moisture trapped in the ear canal, creating a moist environment conducive to bacterial or fungal growth, which may lead to an ear infection.
- Over cleaning of the ears, which can scratch the delicate tissues – Especially using cotton swabs or other objects that can push wax deeper into the ear canal or cause abrasions to the delicate ear canal skin, can disrupt the natural protective layer of wax and increase the risk of irritation, infection, or injury to the ear.
When should I bring my kids to see the doctor?
Ear infection may be getting worse if symptoms persist or intensify despite home care, parents need to alert that these situations require medical attention.
- Persistent ear pain or discomfort
- High fever (above 39 degree Celcius)
- Fluid drainage/ fluid discharge from ears
- Hearing problems
- Unable to balance their body when walking or sitting
- Symptoms is not improving within 2-3 days
REFERENCES
Services, D. of H. & H. (n.d.). Ear infections. Www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au. Retrieved July 16, 2024, from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/ear-infections#causes-of-ear-infections
Mayo Clinic. (2021, June 23). Ear infection (middle ear) – Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ear-infections/symptoms-causes/syc-20351616


