
Fungal Rash In Baby
Fungal Rash Alert: Recognizing, Treating, and Preventing Infections
Fungal rash: A quite common rash that occurs as a result of a fungal infection and can appear on various parts of the skin, including the scalp. These rashes can affect different areas of the body and may cause discomfort, itching, and irritation. Understanding the types, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention.
The common type of Fungal Rash
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): A circular, red, scaly rash with a clear center that resembles a ring. Trichophyton or Microsporum causes this.

Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (n.d.). Ringworm (body). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved [16102024], from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ringworm-body/symptoms-causes/syc-20353780
2. Scalp Ringworm (Tinea Capitis): This rash occurs on the scalp and causes hair loss. Fungal spores spread through direct contact or sharing personal items like combs and hats.
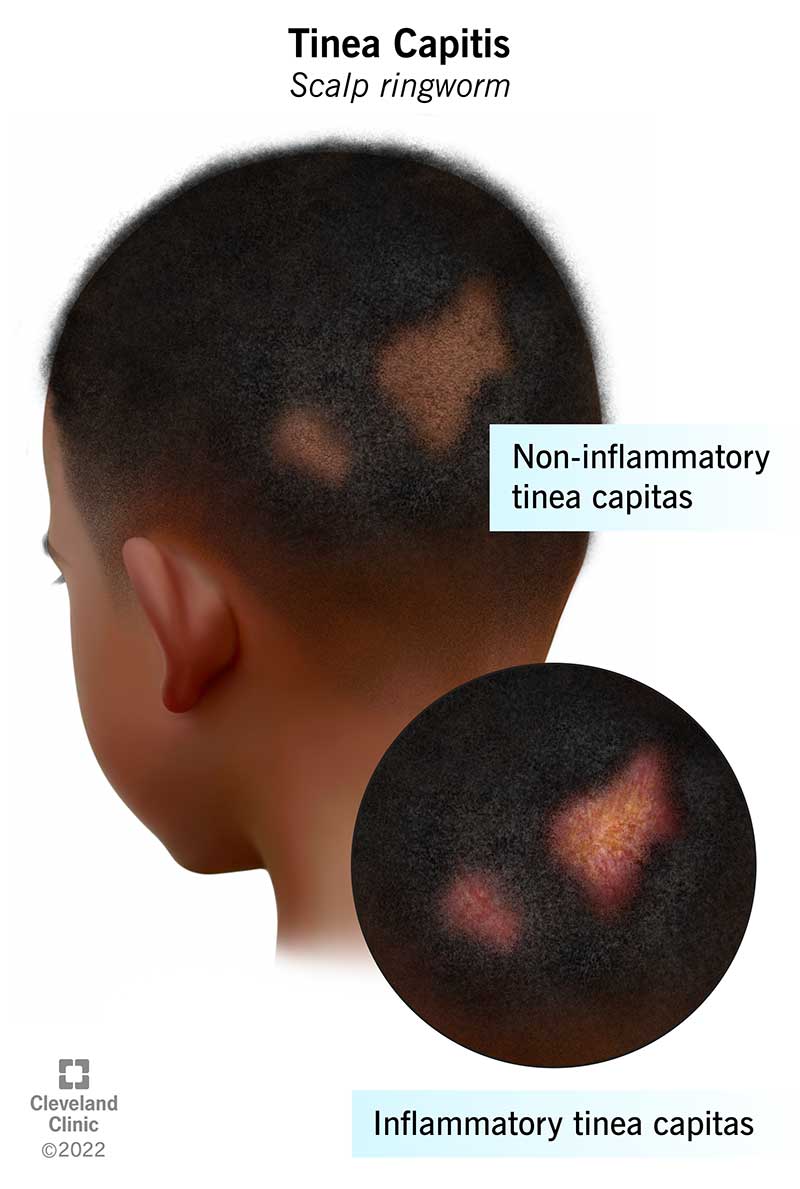
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Tinea capitis: Symptoms, causes & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved [16102024], from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22449-tinea-capitis
3. Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): This common fungal infection often spreads when people walk barefoot in public spaces like bathrooms or locker rooms. The skin between the toes becomes white and peels. An athlete’s foot can also affect the soles of the feet.
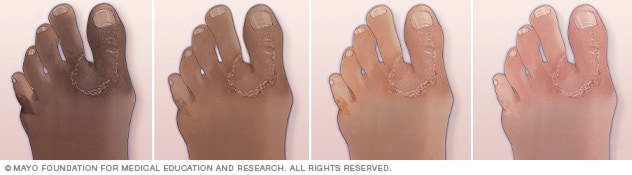
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (n.d.). Athlete’s foot: Symptoms, causes & treatment. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved [16102024], from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/athletes-foot/symptoms-causes/syc-20353841
4. Toenail Fungus ( Tinea Unguium): When toenail fungus is caused by a dermatophyte, it is referred to as tinea unguium. Dermatophytes are molds that require keratin, the protein that makes nails hard, to thrive. These fungi are responsible for approximately 90% of toenail fungal infections. Tinea unguium is also known as onychomycosis.
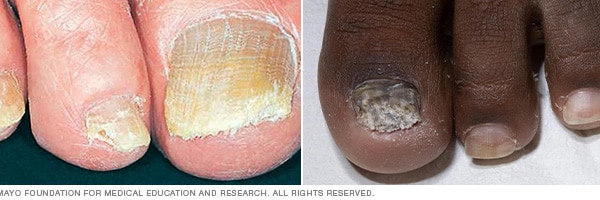
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (n.d.). Nail fungus: Symptoms, causes & treatment. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved [16102024], from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nail-fungus/symptoms-causes/syc-20353294#dialogId47119532
5. Diaper Rash (Candida albicans): The rash usually appears as bright red, inflamed patches in the diaper area, often with raised borders. It may also present with small red bumps or pustules (satellite lesions) surrounding the main rash.
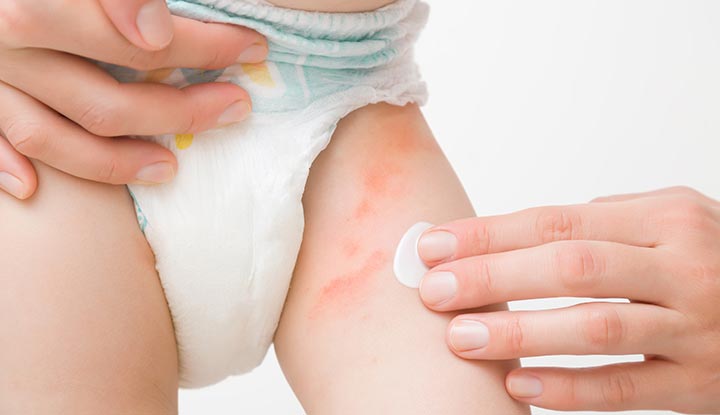

Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Yeast diaper rash: Symptoms, causes & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved [16102024], from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22307-yeast-diaper-rash
Causes and Risk Factors
- Warm and Moist Environments: Fungi thrive in areas that are warm and moist. Sweating, tight clothing, and lack of ventilation can create favorable conditions.
- Poor Hygiene: Infrequent bathing or not drying the skin properly can promote fungal growth.
- Shared Personal Items: Sharing towels, clothing, combs, or sports equipment can spread fungal spores.
- Weakened Immune System: Children with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Use of Antibiotics: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms on the skin, allowing fungi to overgrow.
Treatment
– Topical Antifungal Medications
-Oral Antifungal Medications
-Proper hygiene practices
- Keeping the skin dry is crucial as the fungi thrive in moisture
- Frequent washing and thorough drying of the skin
- Regularly changing and washing clothes
-Regularly clean surfaces and objects that may harbor fungal spores and use an antifungal spray in areas that are prone to moisture.
It’s important for your doctor to look at the rash, especially if it’s your first time having it. They can identify the problem and suggest the best treatment. Using an anti-itch cream that contains steroids might make a fungal rash worse and harder to treat.
Prevention
- Good hygiene
- Keep skin dry
- Use breathable fabrics
- Avoid sharing personal items such as clothes, towels, combs, or other personal items.
- Manage sweating by encouraging children to change out of sweaty clothes immediately after activities.
Fungal rashes in children are generally treatable with proper hygiene and antifungal medications. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the spread and recurrence of infections. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan, especially if the rash is persistent or severe.
References
Skin Fungus: Fungal Infection, Fungal Rash, Skin Fungus Treatment. (2020, September 25). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4276-skin-fungus
Mayo Clinic. (2022, April 26). Ringworm (body) – symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ringworm-body/symptoms-causes/syc-20353780
Tinea Capitis: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment. (2022, March 3). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22449-tinea-capitis
Mayo Clinic. (2022, October 8). Athlete’s foot – Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/athletes-foot/symptoms-causes/syc-20353841
Nail fungus – Symptoms and causes. (2024). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nail-fungus/symptoms-causes/syc-20353294#dialogId47119532
